Getting started: CTL - Configurable Tool Links
- Getting started: CTL - Configurable Tool Links
Parameter Overview
Three different types of external tools can be integrated in SVS (Schulcloud-Verbund-Software):
- Basic
- OAuth2
- LTI 1.1
Common parameters
These parameters are common for all external tools.
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Name | External tool's name |
| URL | External tool's home page |
| Logo-URL | URL to external tool's logo Supported image types: jpg, png |
| Preview-Url | URL to external tool's logo preview image Supported image types: jpeg, png, svg, pdf, bmp, webp, gif, heic, heif, tiff |
| Base-URL | External tool's base launch URL |
For media configuration the following parameters exists:
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Medium-Id | Unique id of the referenced external medium |
| Mediumkatalog-Id | Unique id of the media source for the external medium |
Basic parameters
There are no specific parameters defined.
OAuth2 Parameters
The following parameters are available for tools that authenticate via OAuth2.
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
| ClientId | Public identifier for the client application that wants to access the user's protected resources. It is used to authenticate the client to the authorization server and to obtain the user's consent. The clientId is usually a 32-character hex string that is unique across all clients that the authorization server handles. The clientId is also used to specify the scope, redirect URL, and grant type of the authorization request. |
| ClientSecret | Secret password that only the client application and the authorization server know. It is used to authenticate the client and prevent unauthorized access to the user's protected resources. The clientSecret must be random, unique, and securely stored by the client. The clientSecret is not required for public clients that do not have a secret, such as mobile or single-page apps. |
| Redirect-URLs | Redirect URLs are used to send the user back to the client application (in our case the CTL tool) after they authorize the application to access their protected resources. The redirect URL also contains an authorization code or an access token, depending on the grant type, that the client application can use to obtain the user's data. The redirect URL must be registered with the authorization server when the client application is created, and it must match the URL that is sent in the authorization request. This is to prevent unauthorized redirections to malicious sites that could steal the user's credentials or data. |
| Token Endpoint Auth Method | The OAuth2 parameter "Token Endpoint Auth Method" specifies the authentication method that the client application uses to obtain an access token from the authorization server. SVS supports the following authentication methods: • client_secret_basic The client uses HTTP Basic authentication to send its client ID and client secret in the Authorization header of the token request. • client_secret_post The client sends its client ID and client secret as form parameters in the token request body. The authentication method can be specified when registering an OAuth 2.0 client application with the authorization server, or it can be dynamically requested by using the token_endpoint_auth_method parameter in the authorization request. The authorization server may support one or more authentication methods, and it may reject requests that use an unsupported method. |
| Scope | This parameter limits an application's access to a user's account. It is a parameter that the application can request and the user can grant or deny in the authorization process. The scope defines what the application can and cannot do with the user's data or resources. For example, an application may request the read scope to view the user's profile, or the write scope to modify the user's profile. Different services may define different scopes for their APIs, depending on their needs and architecture. Currently available scopes (migrated from legacy LTI Tools): • iframe (Only useful for BetterMarks) • name • userId • schoolId • groups (Only useful for Nextcloud) |
| Frontchannel Logout URL | Authorization server can use this URL to notify the client application that the user has logged out of the server. This allows the client to perform any necessary actions, such as clearing the session or displaying a logout confirmation message. The Frontchannel Logout URL is usually an endpoint on the client application that accepts a GET request with a parameter called sid, which is the session ID of the user. |
LTI 1.1 Parameters
The following parameters are available for tools that supports the LTI 1.1 standard.
Configuration:
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Key | This is a required parameter that identifies the Tool Consumer that is launching the tool (e.g. SVS). The value of this parameter is a string that is agreed upon by the Tool Consumer and the Tool Provider. The Tool Provider uses this parameter to verify the authenticity and integrity of the launch request. |
| Secret | This is a required parameter that is used together with the key parameter to sign the launch request. The value of this parameter is a string that is agreed upon by the Tool Consumer and the Tool Provider. The Tool Provider uses this parameter to verify the authenticity and integrity of the launch request. |
| Message Type | This parameter indicates the purpose and format of the launch request from the platform to the tool. There are two main types of messages in LTI 1.1: basic-lti-launch-request This is the most common type of message, which initiates a basic launch of the tool with the user's context and role information. The tool can then provide a personalized and interactive experience for the user. LtiResourcelinkrequest Initiates a launch of the tool with the user's context and role information, and provides a personalized and interactive experience for the user. LtiDeepLinkingRequest Initiates a process where the tool provides a list of content items that the platform can embed or link to in its user interface. The content items can be files, images, videos, quizzes, assignments, or any other resources that the tool supports. The platform can then present the content items to the user in a way that is consistent with its own design and functionality. |
| Resource Link Id | A Resource Link Id is identifier for a placement of an LTI resource link within a context that is stable and locally unique to the deployment_id. This value must change if the link is copied or exported from one system or context and imported into another system or context. This allows the Tool Provider to differentiate among different links within the same context. |
| Language | The language parameter in LTI 1.1 is launch_presentation_locale. It is an optional parameter that indicates the locale preference of the user launching the tool. The value should be a language tag as defined by RFC 5646. For example, en-US for American English, fr-CA for Canadian French, or de-DE for German. The Tool Provider can use this parameter to localize the user interface of the tool according to the user's preference. |
| Privacy | The privacy parameter in LTI 1.1 is a custom parameter that allows the Tool Consumer to control the level of personal information that is sent to the Tool Provider. The possible values are: Anonymous No personal information is sent, only a unique and consistent user ID. Pseudonym Users pseudonym is sent. Name User's full name is sent, but not the email address. User's email address is sent, but not the full name. Public Both the user's full name and email address are sent. The privacy parameter is optional and the default value is public. The Tool Provider can specify the minimum level of privacy it requires in the launch request. If the Tool Consumer does not meet the minimum level, the launch request will fail. |
Transmitted parameters:
| Parameter name | Description | Anonymous | Pseudonym | Name | Public | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lti_message_type ⭐ | One of: • basic-lti-launch-request (this is the only one that is supported at the moment, so having the other ones does not make sense) • LtiResourceLinkRequest • LtiDeepLinkingRequest | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| lti_version ⭐ | Always "LTI-1p0" | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| resource_link_id ⭐ | The context id (e.g. course id or board element id) when not overridden by the "Resource Link Id" from the configuration. (This behavior should probably be changed and use the context external tool id) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| launch_presentation_document_target 🔴 | Always "window" | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| launch_presentation_locale 🔵 | "Language" from the configuration | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| roles 🔴 | all roles a user has (SVS => LTI): User => Learner Student => Learner Teacher => Instructor Administrator => Administrator Superhero => Administrator | ❌ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| lis_person_name_full 🔴 | the users full name, when the "Privacy" is "name" | ❌ | ❌ | ✓ | ❌ | ✓ |
| lis_person_contact_email_primary 🔴 | the users email address, when the "Privacy" is "email" | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✓ | ✓ |
| user_id 🔴 | the user's internal id or pseudonym, when the "Privacy" is "pseudonym" | ❌ | ✓ pseudonym | ✓ user id | ✓ user id | ✓ user id |
⭐ required parameter 🔴 recommended 🔵 optional
Custom parameters
Additionally SVS supports custom parameters for external tools which can be required for a specific tool.
Superhero can define an unlimited number of such parameters for each external tool.
SVS differentiates between 3 areas of validity of a parameter (scope):
- global - Valid for the whole SVS instance
- school - Valid within a school
- context - Valid within a specific context
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Name | Mandatory Parameter name |
| User friendly name | Mandatory Name of the parameter to display to the user |
| Comment | Explanation for the parameter for the user |
| Type | Mandatory The following parameter types are supported: String, Number, Boolean, Context Id, Context name, School Id, Official school number The values for Context Id, Context name, School Id, Official school number are determined automatically by SVS during runtime. |
| Scope | Mandatory The following scopes are defined in SVS: global, school, context |
| Location | Mandatory Location for the parameter: path, query, body, anchor |
| Default | Default value |
| Regex | Regular expression to check if a parameter is valid |
| Regex description | Explanation what the regular expression (if any) checks |
Custom parameters that are automatically filled by SVS during runtime (e.g. Context Id, ...) have to be of scope global and cannot have a default value. Some of these parameter types can be without a value (undefined) in certain cases, e.g. the official school number is not a mandatory attribute of a school. If the value is undefined, then the parameter is not part of the launch request and if the parameter is a required parameter, then the launch request fails and an error is displayed.
CTL configuration in SHD
Introduction
This section provides some hints on how to configure the CTL-Tools in the Super Hero Dashboard (SHD).
Glossary
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Medium | An external content that is made available in the SVS client with the help of a CTL-Tool. |
| Metadata | A subset of CTL tool attributes that describe an external content. These include: • name • description • images • publisher |
| Catalog-Id | Unique Id of an external source for media (Medienkatalog / Medienverwaltung / Medienquelle). |
| Medium-Id | Unique Id of an external content within the associated external source. |
| CTL-Template | CTL tool, which is used to create other CTL tools. |
| CTL-Draft | CTL tool that cannot be started. |
Error messages
The display of the error messages in the SHD is not user-friendly.
As a rule, however, you can see the cause of the problem in the error text, see the example below:
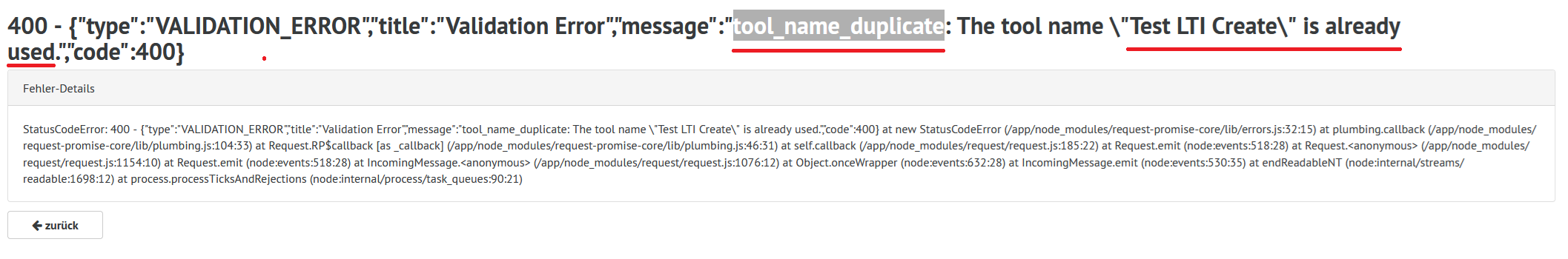
Tool name ambiguity
The name of a tool must be unique.
Automatically ensure unique names
Metadata sync
Metadata from tools that reference external media is automatically updated at regular intervals.
This background synchronization tries to ensure the uniqueness of the tool names.
In the event of a conflict, the tool name is enriched by appending the media ID to achieve uniqueness.
Example:
Abcd – [12345]
Tool provisioning
When creating CTL-Tools based on CTL-Templates, it can happen that the metadata of the tools cannot be updated.
This can happen, for example, if the required external interface cannot be reached temporarily. In this case, a CTL-Draft is created instead of a CTL-Tool.
The name of the tool draft is formed as follows:
Draft: 'catalog-id' 'medium-id'
Example:
Draft: https://www.bildungslogin-test.de/api/external/univention/media urn:bilo:medium:tonart-5-6-2023-ebook
Logo and preview images
Logos and preview images are visible in the following pages of the SVS-Client:
- Media shelf
- Boards
- Course' Tools tab
Display logic
The following logic was implemented to display CTL-Tool images:
-
Media shelf
Preview image is displayed before logo image and before default image -
Other pages
Logo image is displayed before default image
Storage
Logo images are stored in MongoDB, preview images in S3 storage.
The aim is to save also logos in S3 as well. However, the implementation was stopped because there was no technical solution to call the File-Service in background batches.
Metadata update
Metadata can currently only be updated for the media from the following catalogs:
- Bildungslogin
- VIDIS
Logos and preview images can be updated in SHD by superhero.
In background batches, only logos can currently be updated.
SVG images
Since SVG images can contain potentially harmful components (e.g. scripts), a cleanup of such parts is performed before saving the image.
This can cause the appearance of the image to change after saving.
Medium
The Medium section is used to link a CTL-Tool to an external content. For this purpose, a catalog-ID (source of the content) and a medium-ID must be specified.
CTL-Template
A template is used to automatically create CTL-Tools and assign them to the schools.
If automation is active in a school, then during ad-hoc provisioning, the creation of missing CTL-Tools for media and their assignment to schools is performed.
Only one template can be created per catalog.
Provisioning behavior
School admin can configure provisioning behavior within SVS-Client on the following page:
School-Management > Authentication, edit the "moin.schule" system
(Administration > Manage school > Data synchronization options)
CTL-Draft
CTL draft is a CTL tool that cannot be started.
CTL drafts are not offered to the school administrator for assignment to schools.
Normally, CTL drafts are created during the automatic process of generating CTL tools from templates, namely when the required external interface could not be reached to retrieve metadata of the medium.
Preferred tools
For a preferred tool, an icon must be specified.
Icons listed in the following file are accepted: https://github.com/hpi-schul-cloud/nuxt-client/blob/bb3927f88121a9c8e33499aeac079edd702bc134/src/components/icons/material/index.ts#L1
The maximum number of preferred tools within an SVS instance is defined by the following environment variable: CTL_TOOLS__PREFERRED_TOOLS_LIMIT
Contexts
The use of the media can be restricted to certain areas of the SVS-Client (Contextes).
For example, you can restrict a CTL-Tool only to use on the media shelf or in the boards.
Base URL
The URL is used to start an external tool or to open an external medium.
OAuth2
Client ID and client-secret cannot be changed after the tool has been successfully saved. To make a correction, the tool must be deleted and recreated.
CTL tools import endpoint
A separate endpoint is available for an automated import of a larger number of external tools.
The endpoint is documented here: Swagger-Documentation.